






















































































Computer-Aided Facility Management
Computer-Aided Facility Management (CAFM) is a technology-driven approach to efficiently manage and optimize the use of physical spaces and resources within a facility. It involves the use of specialized software and tools to streamline facility management processes, enhance operational efficiency, and improve decision-making.

Key Components of CAFM:
- Space Management:
- CAFM software allows facility managers to accurately map and visualize the layout of spaces within a facility, including offices, workstations, meeting rooms, and common areas.
- Space management features help organizations make informed decisions about space utilization, occupancy levels, and real estate planning.
Asset Management:
- They provide tools for asset tracking, maintenance scheduling, and lifecycle management to ensure optimal performance and longevity of assets.
- Asset management functionalities help minimize downtime, reduce maintenance costs, and extend the lifespan of critical infrastructure.
Maintenance Management:
- It allows facility managers to create and assign maintenance tasks, track work orders, and monitor the status of maintenance activities in real-time.
- Maintenance management features help organizations improve asset reliability, reduce downtime, and comply with regulatory requirements.
Resource Scheduling:
- They provide scheduling tools that enable users to book resources, manage reservations, and avoid conflicts in scheduling.
- Resource scheduling capabilities help organizations optimize resource utilization, improve productivity, and enhance collaboration among employees.
Energy Management:
- It provides tools for energy benchmarking, consumption analysis, and cost optimization to identify opportunities for energy savings and sustainability improvements.
- Energy management features help organizations reduce energy costs, minimize their environmental footprint, and achieve compliance with energy efficiency regulations.
Reporting and Analytics:
- They enable stakeholders to monitor performance metrics, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to improve operational efficiency and resource allocation.
- Reporting and analytics functionalities help organizations track progress towards their goals, identify areas for improvement, and demonstrate the value of facility management initiatives.


ERP System Management
An ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system is a software solution that integrates and manages core business processes and functions across an organization. ERP systems typically cover areas such as finance, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain management, customer relationship management, and more.
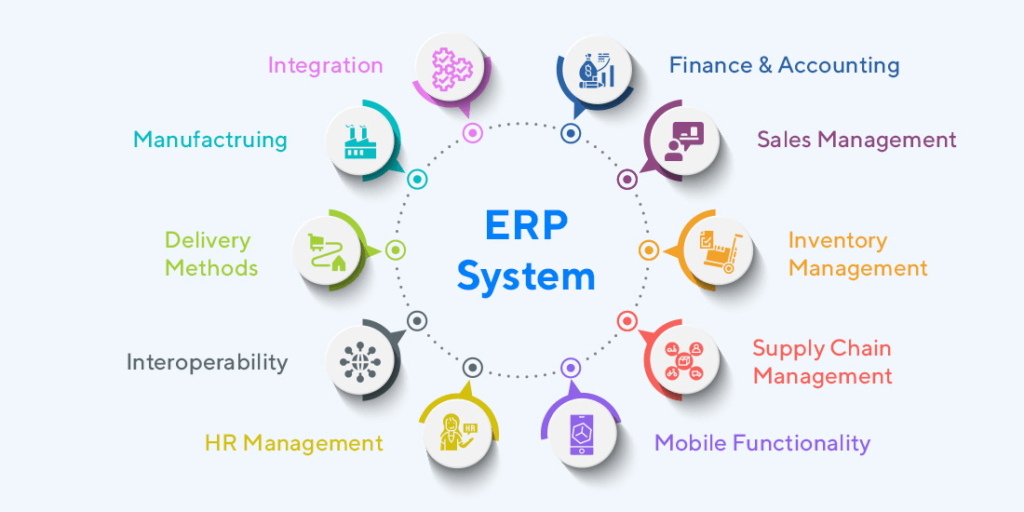
Key Components of ERP
Finance and Accounting: Tracks financial transactions, manages accounts payable/receivable, facilitates budgeting and forecasting, and generates financial reports.
Human Resources (HR): Manages employee data, payroll processing, benefits administration, recruitment, performance evaluation, and training.
Supply Chain Management (SCM): Streamlines procurement, inventory management, order fulfillment, supplier relationship management, and logistics.
Manufacturing: Supports production planning, scheduling, inventory control, quality management, and shop floor operations.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Manages customer data, sales automation, marketing campaigns, customer service, and support.
Business Intelligence (BI) and Reporting: Provides analytics, reporting tools, and dashboards for data analysis and decision-making.
